New Methods: An AI-Driven Study
Utilizing AI-research tools to design a virtual assistant for job seekers
Project Background
The job search process is broken. Job seekers are overwhelmed by countless applications, vague job descriptions, and unpredictable interview processes. Despite platforms like LinkedIn offering job alerts, resume-building tools, and interview guidance, these features are static, impersonal, and fail to provide the strategic, tailored support job hunters truly need. AI has the potential to change this by offering personalized guidance - helping candidates craft stronger applications, analyze job descriptions for alignment with their skills, and prepare for interviews with tailored coaching. But how can AI be applied effectively to truly improve outcomes for job seekers?
AI is transforming industries, and UX research is no exception. To stay relevant in this rapidly evolving landscape, I utilized AI research tools for this project - learning not only how they work but how they can be applied meaningfully in any research space.
Activities:
AI Discussion Guide Creation
AI Interviewing
Participant Recruitment
AI Analysis
AI Journey Mapping
Tools: ChatGPT, Listen Labs, Marvin, Coloop
Crafting the Discussion Guide: My Process
Generating a Baseline Prompt for the LLM
To start, I asked ChatGPT to generate a structured prompt that I could then feed back into the model. This prompt needed to clearly define the research objective, the target audience, and the type of questions I was looking for. The goal was to ensure the AI understood the context and could generate relevant discussion questions for the study.Using the Prompt to Generate an AI-Drafted Discussion Guide
With the refined prompt, I had ChatGPT generate a full discussion guide. This included a variety of potential questions covering different aspects of the job-hunting experience and how an AI assistant might help. The AI provided a structured starting point, ensuring I wasn’t starting from scratch.Reviewing, Selecting, and Refining Questions
AI-generated content isn’t perfect, and human oversight is crucial. I carefully reviewed the discussion guide, selecting the most relevant questions and rewording some to ensure clarity and alignment with the research goals. This step allowed me to filter out redundant or irrelevant questions while improving the phrasing to make them more natural and engaging for participants.Testing the Guide Through AI-Simulated Responses
To refine the guide further, I asked ChatGPT to act as a participant and respond to the questions. This allowed me to assess how well the questions flowed, whether they prompted useful insights, and if any needed further clarification or adjustment.Iterating Based on AI Responses
As I reviewed the AI-generated responses, I identified areas where questions could be more precise, engaging, or open-ended. I tweaked wording and structure as needed, ensuring that the final discussion guide was both clear and capable of eliciting valuable insights.
AI-Driven Interviews: Exploring the Potential and Limitations
To test the effectiveness of AI in moderating interviews, I used ListenLabs to conduct structured interviews with job seekers. I refined my discussion guide by prioritizing key follow-up questions and recruited six participants through my LinkedIn network. Participants described their experience with the AI moderator as "interesting," but I observed several limitations in how it handled responses.
The AI struggled to adjust when participants answered later questions earlier in the discussion, often repeating itself instead of adapting. While it followed a structured script well, it lacked the ability to probe deeper or recognize when a different line of questioning was needed. These limitations highlight the strengths and weaknesses of AI-driven interviews compared to human-led sessions.
AI vs. Human Moderation
When AI Interviews Work Well:
Collecting data quickly from a large number of participants
Conducting interviews under time constraints
Facilitating interviews in languages the researcher does not speak
Why Human Interviews Are Still Better:
Flexibility to adjust questions based on responses
Ability to probe deeper into unexpected insights
Stronger rapport, leading to more candid answers
AI-driven interviews offer efficiency and scalability, but for deeper insights and nuanced discussions, human moderation remains the stronger approach.
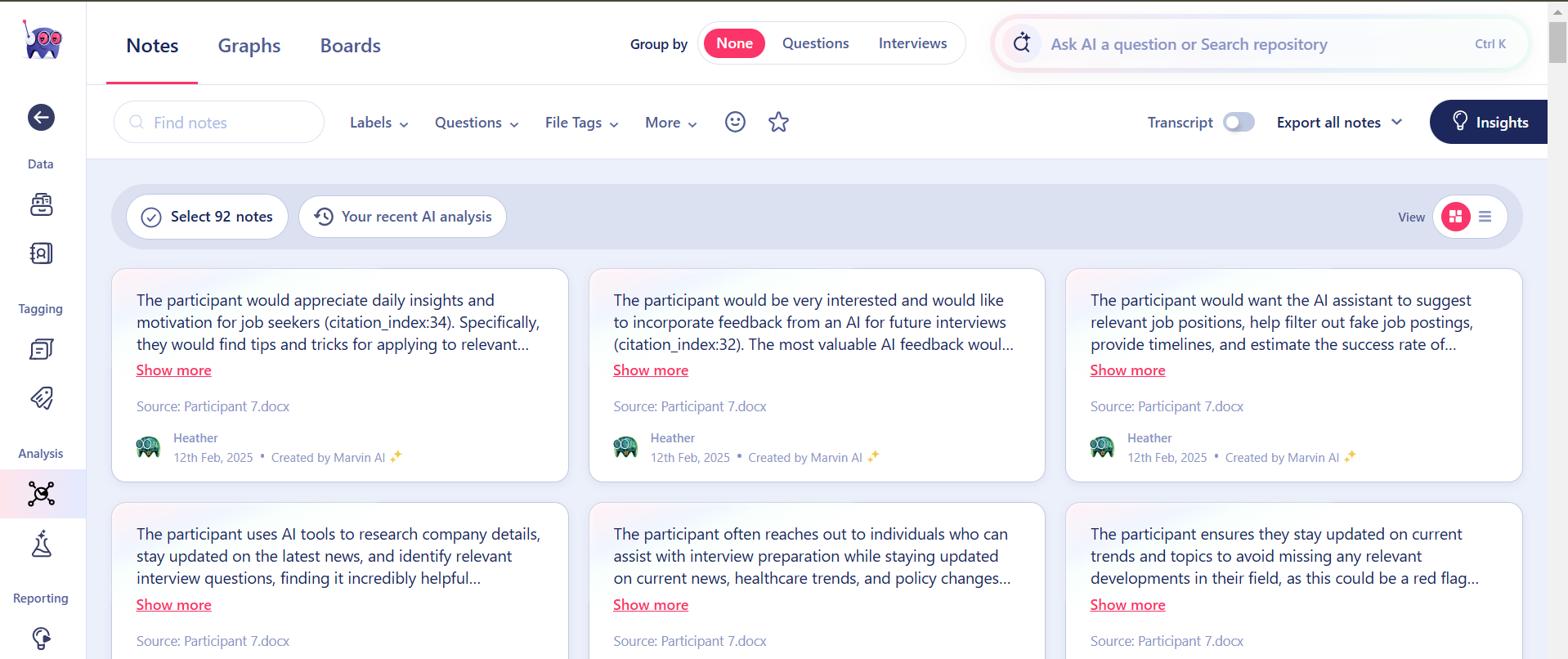
Comparing AI-Powered Analysis Tools
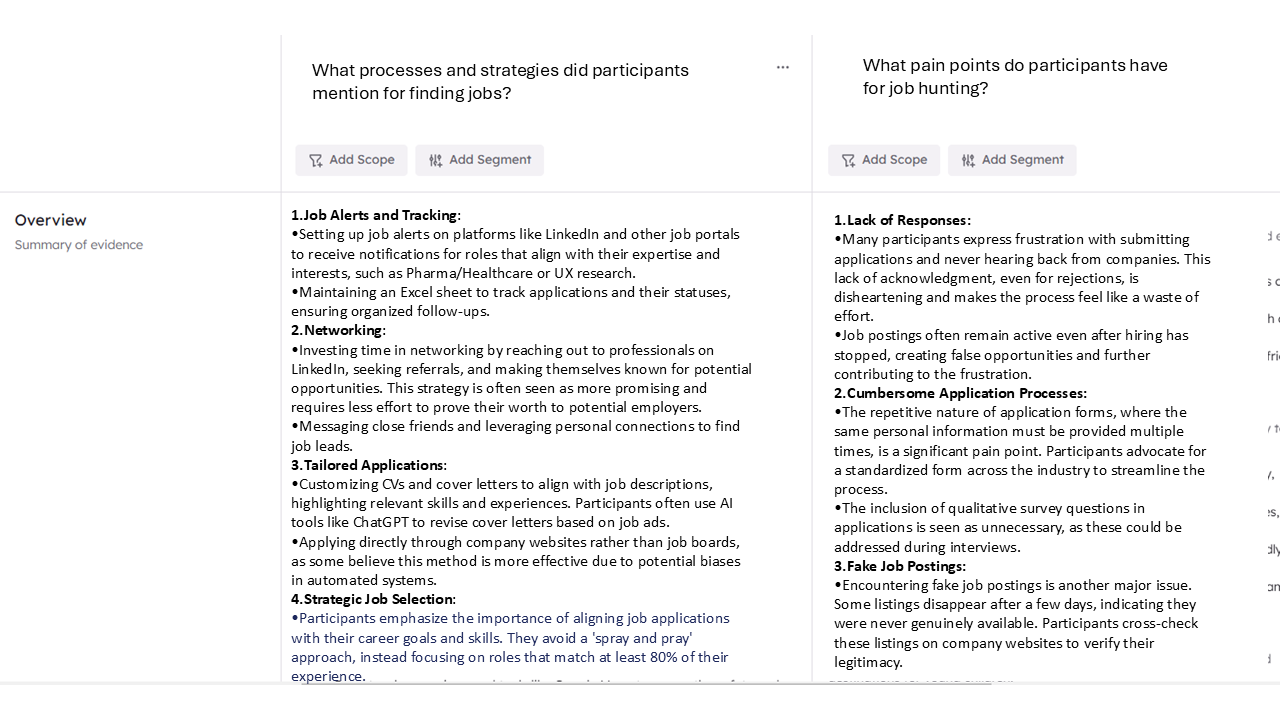
To evaluate how different AI tools process interview data, I analyzed the same set of responses using Listen Labs, Marvin, and Coloop. Each tool provided valuable insights but in distinct ways, highlighting their unique strengths and limitations.
ListenLabs stood out for its visual representations, making it easier to spot trends at a glance. Marvin excelled at ensuring balanced analysis, avoiding the tendency to overemphasize themes based on a small number of responses. Coloop provided a clear and structured way to view supporting quotes and data, making it especially useful for referencing specific participant feedback. I also appreciated Coloop’s ability to generate questions for the data.
Listen Labs
Marvin
Coloop
Results:
While analyzing the data, I identified the foundational structure of a job search journey map. To enhance this, I leveraged ChatGPT to generate experience scale ratings based on the raw data. Using a previously developed template, I was able to draft the journey map below in under four hours—a process that would have taken me nearly two weeks if done manually. However, I would suggest validating this further with users before moving forward with any concepts. The experience scale here seems especially suspicious.
Top Five AI Solutions for Job Hunting
Automated Job Search & Filtering
AI can match job seekers with relevant roles based on skills, experience, and preferences while filtering out expired, fake, or low-quality postings to improve job search efficiency.Resume & Cover Letter Optimization
AI can analyze job descriptions, suggest relevant keywords, and refine language to help applications pass Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) and better align with employer expectations.Interview Question Practice & Feedback
AI can generate job-specific interview questions, evaluate responses for clarity and relevance, and provide constructive feedback to improve performance and confidence.Application Automation
AI can auto-fill repetitive application forms, track application statuses in one dashboard, and streamline the entire process, saving job seekers time and reducing frustration.Career Path Guidance & Skill Development
AI can analyze market trends, identify in-demand skills, and recommend courses or certifications to help job seekers adapt to industry shifts and explore alternative career paths.
Conclusion:
This study highlights the powerful potential of AI as a tool for accelerating and operationalizing research. From synthesizing data to generating structured outputs like journey maps, AI can significantly reduce the time and effort required for analysis. However, while AI is an incredibly useful assistant, it is not a replacement for human judgment.
The research process requires thoughtful refinement, contextual understanding, and critical thinking—things AI cannot fully replicate. While AI can quickly surface patterns and provide a strong starting point, it takes a human researcher to interpret, refine, and extract the most meaningful insights. Relying solely on AI risks losing the depth, nuance, and strategic thinking that make research truly valuable.
Ultimately, the most effective approach is AI-assisted research, not AI-driven research. AI should be leveraged in the right scenarios—speeding up repetitive tasks, generating structured outputs, and assisting with synthesis—but always with human oversight to ensure quality, relevance, and impact.